Understanding Shoulder Pain and Its Connection to External Rotation
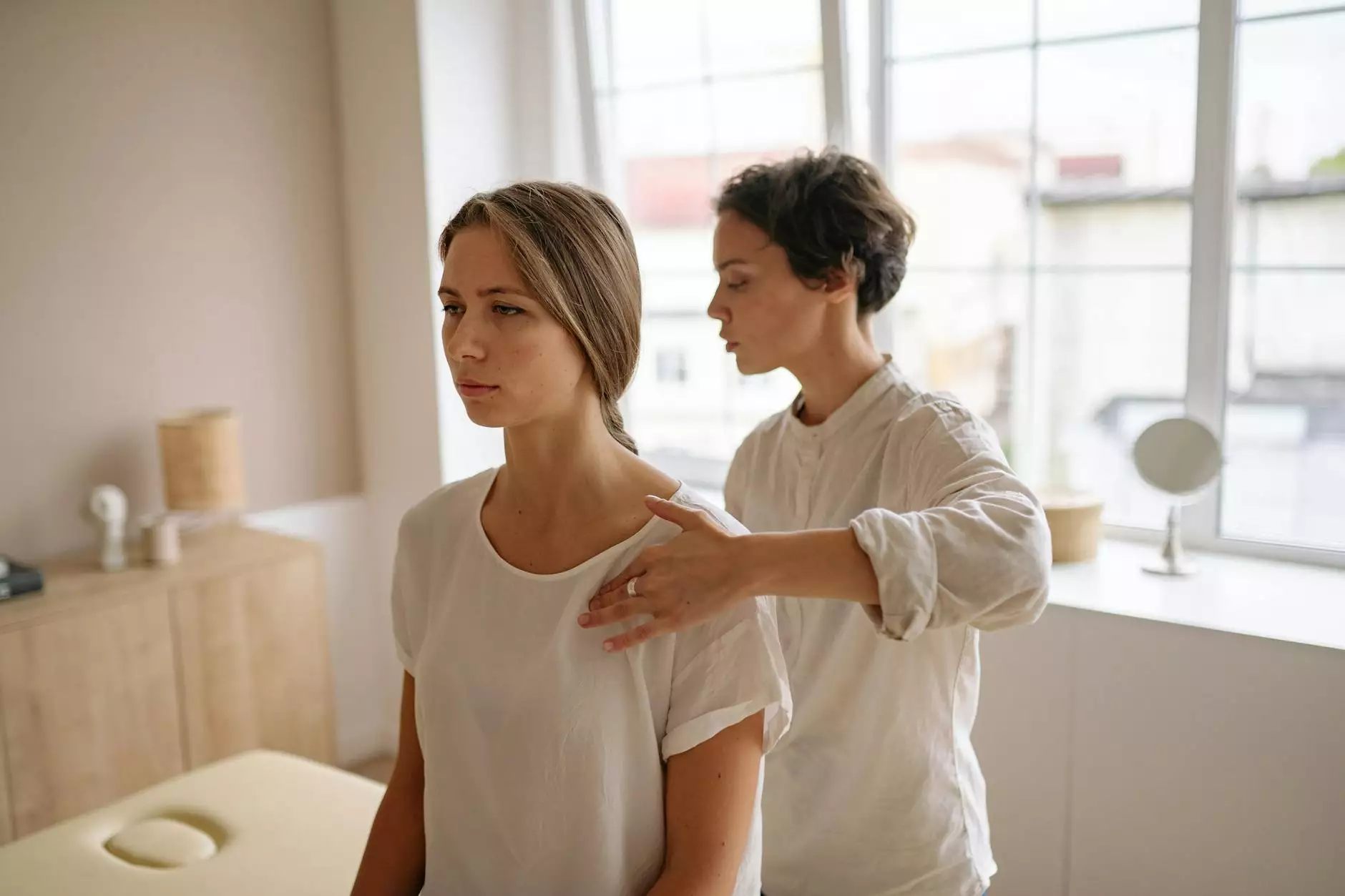

Shoulder pain is a common ailment that affects people of all ages, and one of the key movements involved in shoulder mechanics is external rotation. Understanding the relationship between shoulder pain and external rotation is essential for effective diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of shoulder pain, its causes linked to external rotation, and how to manage and treat this condition.
The Anatomy of the Shoulder
The shoulder is one of the most flexible joints in the human body, allowing a wide range of motion. The joint includes three major bones: the humerus, the scapula, and the clavicle. The shoulder joint, or glenohumeral joint, consists of:
- Glenoid Cavity: A shallow socket in the scapula that houses the head of the humerus.
- Rotator Cuff: A group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder and enable rotation.
- Ligaments: Connective tissue that provides stability to the joint.
What is External Rotation of the Shoulder?
External rotation refers to the movement that rotates the shoulder joint outward, away from the body. This motion is crucial for numerous activities, from sports to daily tasks like reaching for an object or throwing. The primary muscles involved in shoulder external rotation include:
- Infraspinatus: A major muscle of the rotator cuff that plays a vital role in shoulder mobility.
- Teres Minor: This muscle aids in the external rotation of the shoulder joint.
- Deltoid: Helps in the overall movement of the shoulder, assisting with external rotation.
Common Causes of Shoulder Pain Associated with External Rotation
Shoulder pain can stem from various conditions, many of which are linked to restricted or painful external rotation. Some of the most common causes include:
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: Tears, strains, or inflammation in the rotator cuff can severely limit external rotation.
- Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder): A condition that causes stiffness and reduces mobility, leading to pain during external rotation.
- Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: Occurs when shoulder tendons are compressed during arm lifting, causing pain, especially during external rotation.
- Labral Tears: Tears in the cartilage of the shoulder may lead to pain and instability during rotation movements.
- Arthritis: Inflammatory conditions can disrupt joint function and lead to pain during rotation.
Symptoms of Shoulder Pain Related to External Rotation
Recognizing the symptoms is crucial in determining the cause of shoulder pain associated with external rotation. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Often felt in the upper arm or shoulder area, exacerbated by movement.
- Weakness: Difficulty lifting the arm or performing overhead activities.
- Stiffness: Limited range of motion during arm movements, particularly in external rotation.
- Clicking or Popping Sounds: Noises experienced during shoulder movements can indicate underlying issues.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the shoulder can contribute to discomfort and reduced mobility.
Diagnosis of Shoulder Pain
A thorough diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Medical professionals may employ various diagnostic methods, including:
- Physical Examination: Evaluation of shoulder range of motion and pain areas.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds to visualize soft tissues and bone structures.
- Functional Tests: Assessing the shoulder’s functional capacity and ability to perform external rotation.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Pain Related to External Rotation
Treatment of shoulder pain associated with external rotation is often multifaceted. Here are some common approaches:
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of treatment, focusing on exercises that restore range of motion, strength, and function. Specific external rotation exercises may include:
- External Rotation with Resistance Bands: Strengthening the rotator cuff muscles.
- Wall Angels: Improving mobility and flexibility.
- Scapular Stabilization Exercises: Enhancing stability in shoulder movements.
2. Medication
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, doctors may recommend steroid injections.
3. Surgery
For persistent cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical options may be considered. Procedures might involve:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: Repairing tears or removing impinging tissue.
- Shoulder Replacement: In severe arthritis cases, replacing damaged joint surfaces may be necessary.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to formal treatments, several home remedies and lifestyle adjustments can aid recovery:
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to reduce swelling and numb pain.
- Heat Therapy: Warm compresses can ease stiffness before exercises.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Modifying workspaces to prevent overexertion of shoulder muscles.
Prevention of Shoulder Pain and Maintenance of Shoulder Health
Preventing shoulder pain is crucial, especially for individuals engaged in repetitive overhead activities. Consider these preventive measures:
- Strength Training: Regularly engaging in strength training for upper body muscles, focusing on the rotator cuff.
- Flexibility Exercises: Incorporating stretching routines to maintain shoulder flexibility, especially during warm-ups.
- Proper Techniques: Using correct techniques in sports or physical activities to minimize injury risks.
The Role of Chiropractors in Managing Shoulder Pain
Chiropractors can play a vital role in the management of shoulder pain associated with external rotation. Chiropractic care may include:
- Manual Adjustments: Aligning the spine and shoulder joints to improve function.
- Soft Tissue Therapies: Techniques like massage to relieve muscle tension and enhance mobility.
- Guided Rehabilitation: Customized exercise programs tailored to individual needs.
Conclusion
Shoulder pain related to external rotation is a significant concern that requires understanding of the underlying mechanisms. By recognizing the symptoms, diagnosing properly, and pursuing comprehensive treatment options—including physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes—individuals can effectively manage their pain and regain functional mobility. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, including chiropractors, is essential for crafting a personalized approach to recovery and long-term shoulder health. Remember, a proactive strategy not only helps alleviate pain but also contributes to enhanced quality of life.
shoulder pain external rotation